| wingCellType Complex Type |
Cell of the wing
Namespace: Empty
Schema: Empty
| Name | Occurrences | Description |
|---|---|---|
| | Spanwise positioning of wing cells. | |
| | Chordwise positioning of wing cells. | |
| | Spanwise positioning of wing cells. | |
| | Chordwise positioning of wing cells. | |
| | Material properties of the wing skin. | |
| | [0, 1] | Definition of the wing stringers. |
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes |
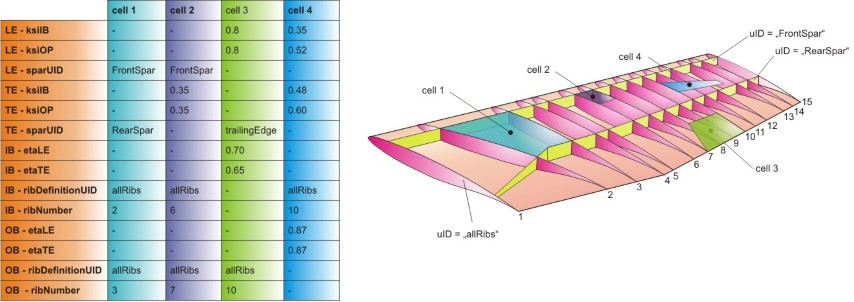
A cell defines a special region of the wing. Within this region skin and stringer properties can be defined that differer from the properties of the rest of the wing. In general a cell is defined by defining four borders – the cell leading and trailing edge and the inner border and the outer border. Those borders can either be defined by using eta/xsi coordinates or by referencing to spars and ribs. Mixed definitions (e.g. forward border is defined due to a spar, side borders due to eta coordinates) is allowed. In general a cell is quadrilateral. But if e.g. the spar, which is used for the definition of the trailing edge, has a kink, the cell can have more than four corners.
The cell leading and trailing edge (= forward and rear border) can either be defined by referencing to a spar (->sparUID) or by the defining the xsi (=relative chord) coordinates of the border (xsi1 = inner end; xsi2 = outer end).
The cell inner and outer border can either be defined by referencing to a rib (->ribDefinitionUID and ribNumber) or by the defining the eta (=relative spanwise) coordinates of the border (eta1 = forward end; eta2 = rear end).
Some examples for wing cells can be found in the picture below: